Introduction to Wire Gauges
When it comes to electrical engineering and design, the selection of the appropriate wire gauge is of paramount importance. Wire gauges, also known as wire sizes, are standardized measurements of the diameter of a wire. Understanding the numbering system and the potential engineering uses for each gauge is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of wire gauges and explore the engineering applications associated with different sizes.
The Numbering System of Wire Gauges
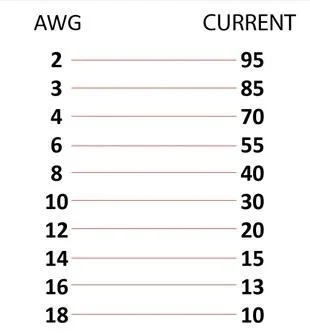
Wire gauges are typically measured using either the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system or the Standard Wire Gauge (SWG) system. However, the AWG system is the most commonly used standard in the United States and Canada. In the AWG system, the gauge number is inversely related to the diameter of the wire. This means that the higher the gauge number, the smaller the wire diameter. For instance, a 10-gauge wire is much thicker than a 20-gauge wire.
Exploring Wire Gauges: AWG 08-24
At our company, we specialize in wire gauges ranging from AWG 08 to AWG 24. The selection of the appropriate wire gauge is crucial for the successful implementation of electrical systems. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of wire gauges within this specific range and explore the engineering applications associated with different sizes.
The Numbering System of Wire Gauges
As mentioned previously, In the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, the gauge number is inversely related to the diameter of the wire. This means that a lower gauge number corresponds to a thicker wire diameter, while a higher gauge number indicates a thinner wire. Within our focus range of AWG 08 to AWG 24, we encounter a variety of wire sizes that find applications across a broad spectrum of engineering needs.
Engineering Uses for Different Wire Gauges within the AWG 08-24 Range
AWG 08-10 Gauge
Wire gauges in the range of AWG 08 to AWG 10 are relatively thick and are often used in applications where high electrical current and power transmission are required. These gauges are suitable for use in heavy-duty equipment, industrial machinery, and large-scale electrical installations.
AWG 12-14 Gauge
Wire gauges in the AWG 12 to AWG 14 range are commonly used for general electrical wiring in both residential and commercial settings. They find applications in power distribution, lighting systems, and various electrical appliances.
AWG 16-18 Gauge
Within the range of AWG 16 to AWG 18, we encounter wire gauges that are suitable for a wide range of applications, including branch circuit wiring, internal wiring of electrical panels, and motor leads in industrial equipment.
AWG 20-24 Gauge
Thinner wire gauges in the range of AWG 20 to AWG 24 find use in applications where flexibility and space constraints are critical. They are commonly employed in electronic devices, control circuits, and telecommunications equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wire gauges play a critical role in a wide array of engineering applications, ranging from heavy-duty power transmission to delicate electronic circuitry. Understanding the numbering system and the engineering uses associated with different wire gauges is essential for selecting the most suitable wire for a specific application. By considering factors such as current-carrying capacity, voltage drop, and mechanical strength, engineers can ensure the optimal performance and safety of electrical systems. Whether it’s powering industrial machinery or enabling the functionality of miniature electronic devices, the selection of the right wire gauge is fundamental to the success of any engineering project.